Week 1:
Question 1
R can perform several forms of statistical
computation. What is an example of hypothesis testing?
1 point
Compute and visualize a correlation matrix among
four different variables to see if they are correlated.
Inferring an unknown mean value of a population
from its samples.
Obtaining a representative subset of data.
Testing if the mean values of two groups are
statistically different.
2.
Question 2
Which of the following data type conversions may
be not allowed in R?
1 point
logical (like TRUE or FALSE) to numeric
integer (like 1L or 2L) to numeric
character (like `1`, `A`, or `test`) to numeric
numeric (like 1 or 2) to integer
3.
Question 3
What is the result of the R expression 100 * (5 – 3)?
1 point
200
503
497
500
4.
Question 4
After you write code in an R script file or the
R Console, what component of the R environment parses the code into objects in
memory?
1 point
R variables, functions, and datasets
R Interpreter
R data files
R Workspace
5.
Question 5
Which features of RStudio help facilitate code
writing? Select two answers.
1 point
File Explorer
Syntax highlighting
Workspace visualization
Code auto completion
6.
Question 6
True or False: Execution order does not matter
when executing cells in a Jupyter notebook
1 point
True
False
Week 2 :
1.
Question 1
What is a nominal factor?
1 point
A factor with any type or number of elements.
A factor with no implied order.
A factor with ordering.
A factor that contains numeric data.
2.
Question 2
Assume that the variable test_result contains the
vector c(25, 35, 40,
50, 75).What is the
result of the expression mean(test_result)?
1 point
45
50
40
35
3.
Question 3
Assume you have variable called employee that
contains the expression list(name
= “Juan”, age = 30). What is the
correct command to change the contents of the age item to 35?
1 point
employee[age] = 35
employee[“age”] == 35
employee[age] <- 35
employee[“age”] <- 35
4.
Question 4
What is the main difference between a matrix and
an array?
1 point
A matrix can be arranged by rows or columns, but
an array is always arranged by columns.
A matrix can contain vectors, but an array can
only contain strings, characters, or integers.
A matrix must be two dimensional, but an array
can be single, two dimensional, or more than two dimensional.
A matrix can contain multiple types of data, but
an array can only contain data of the same type.
5.
Question 5
Assume that you have a data frame called employee that
contains three variables: name, age, and title. If you want to return all the values in the title variable,
what command should you use?
1 point
employee$title
employee.title
employee[title]
employee[[3]]
Week 3 :
1.
Question 1
What is the result of the conditional statement 25 > 15 | 99 >= 100?
1 point
TRUE
FALSE
2.
Question 2
How do you define a global variable in a
function?
1 point
Use the <- assignment operator.
Use the <<- assignment operator.
Use the == assignment operator.
Use the -> assignment operator.
3.
Question 3
You can use the str_sub() function to
form a substring by counting back from the last position. This function is part
of which package?
1 point
tidyr
stringr
readr
purrr
4.
Question 4
Assume you have a data frame that contains a
string variable called ‘phone’. The phone numbers in this variable appear in
(###) ###-#### or ###-###-#### format. Which feature of R can you use to
isolate the area code (the three numbers between the parentheses or the first
three numbers)?
1 point
A string operation.
A mathematical operation.
A regular expression.
It is not possible to do this using R.
5.
Question 5
When you convert a date in string format to a
Date object, what information do you need to pass to the as.Date() function?
Select two answers.
1 point
The date format of the string.
The string containing the date.
The UNIX format of the string.
The number of days since January 1, 1970.
6.
Question 6
What is the difference between an error and a
warning in you R code?
1 point
You can catch an error, but you cannot catch a
warning.
You can catch a warning, but you cannot catch an
error.
A warning halts code execution, while an error
does not.
An error halts code execution, while a warning
does not.
Week 4 :
1.
Question 1
Assume you have read a .csv file into a data
frame variable called employee. It has 20 rows of data and three variables: name, age, and title. What is the
correct statement to use to return the fifth row of data in the name and title columns?
1 / 1 point
employee[5, c(“name”, “title”)]
employee[c(“name”, “title”), 5]
employee[5, 2:3]
employee[2:3, 1:5]
2.
Question 2
How do you return the number of characters in
each paragraph of a text file that has been read into a character vector?
1 / 1 point
Use the scan() function.
Use the nchar() function.
Use the length() function.
Use the file.size() function.
Question 3
Which package do you need to install before
writing to an Excel file in R?
1 / 1 point
No package is needed. This functionality is
built into R.
writexl
xlsx
writexlsx
4.
Question 4
You want to get a resource by its URL using an
HTTP request and assign the HTTP response containing status code, headers,
response body to a response variable. Which function should you use?
1 / 1 point
response <-HEAD(“https://www.mysite.com”)
response <-POST(“https://www.mysite.com”)
response <- GET(“https://www.mysite.com”)
response <-PUT(“https://www.mysite.com”)
5.
Question 5
After reading an HTML page from a URL, what must
you do to get the <body> node from the root <html> node?
1 / 1 point
Use the html_text() function to return the <body> node of the
HTML.
Use the html_node() function to return the <html> node.
Use the html_text() function to return the <html> node.
Use the html_node() function to
return the <body> as a child node of <html> node.
Final Quiz :
1.
Question 1
Which of the following is a typical way that
developers use the R language?
1 / 1 point
OR
a. Systems programming
b. Web page interactivity
c. Predictive analysis
d. Video game development5b
Answer: c. Predictive
analysis
2.
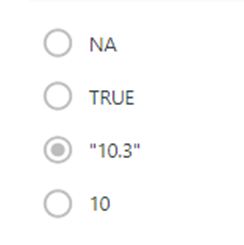
Question 2
In R, what is the result of the function
as.character(10.3)?
1 / 1 point
Expand
3.
Question 3
In R, which command removes a variable from
memory?
1 / 1 point
Expand
4.
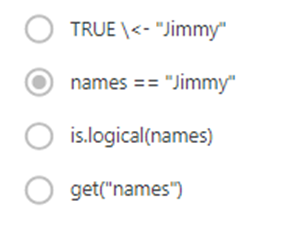
Question 4
In R, assume
a character vector called “names” has the following contents:
"Harry"
"Jimmy" "Tammy"
Which command
would return the following logical vector?
FALSE TRUE FALSE
1 / 1 point
Q5. Assume that the
function add is defined as follows:
add <- function(x,y) { (x + y) return (x – y) temp <<- (x * y) return
(x / y) }
What will be the output if you issue the command add(10,5)?
a. 50
b. 15
c. 2
d. 5
Answer: d. 5
OR
5.
Question 5
In R, assume you have a vector named “age,” and
each element in the vector is the age of one person in a group. The vector has
the following content: 24 32 46 19. What will be the result if you issue the
age[-2] command?
1 / 1 point
6.
Question 6
Assume the
array books_array contains 6 elements. The array has three rows and two columns
and appears as follows:
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "It" "Dr. Sleep" [2,] "Misery"
"Carrie" [3,] "The Shining" "The Mist"
If you input the books_array[,1] command, what
will be the output?
1 / 1 point
Expand
OR
Q6. In R, variables are
typically assigned using <−, but they can also be assigned using which of the
following symbols?
a. =
b. ≠
c. -\>
d. <=
Answer: a. =
7.
Question 7
In R, which command returns the first six elements
of a data object such as a data frame?
1 / 1 point
8.
Question 8
Assume that
the function isReviewGood is defined as follows:
isReviewGood
<- function(rating, threshold = 8) { if(rating < threshold){
return("NO") } else { return("YES") } }
Which of the following commands will return
“YES”?
0 / 1 point
Expand
IsReviewGood(6)
o
IsReviewGood(return, threshold=10)
o
IsReviewGood(rating, 9)
o
IsReviewGood(7.5, threshold = 7)
OR
Q8. In R, assume you have a
vector named “age,” and each element in the vector is the age of one person in
a group. Which command must you use to reorder the ages from youngest to
oldest?
a. call(age)
b. order(age)
c. rank(age)
d. sort(age)
Answer: d. sort(age)
9.
Question 9
What is the first step you must take before you
can read an Excel spreadsheet in R?
1 / 1 point
Expand
10.
Question 10
After installing and calling the httr library in
R, which command can you use to request information about
https://www.google.com?
1 / 1 point
OR
Q10. In R, which command
will output the data from the Nile built-in data set?
a. help(Nile)
b. Nile
c. data(Nile)
d. install.Nile
Answer: b. Nile
OR :
Q12. In R, which command
should you use to insert a new row into a data frame?
a. integrate
b. rbind
c. head
d. tail
Answer: b. rbind
OR
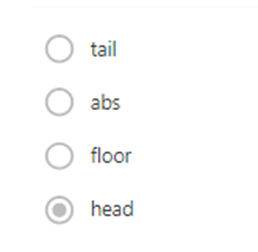
Q13. In R, which command
returns the first six elements of a data object such as a data frame?
a. tail
b. floor
c. abs
d. head
Answer: d. head
OR
Q14. Which of the following
blocks of R code properly defines a function that takes two numbers as input
and returns the product of the two numbers multiplied together?
a. mult \<- function() { x \ * y }
b. mult \<- function(xy) { x \ * y }
c. mult \<- function(x,y) { x \ * y }
d. mult \<- function{ x \ * y }
Answer: c. mult \<-
function(x,y) { x \ * y }
Q15. Which command in R
would return the following numeric vector?
5 4 3 2 1
a. c(5:1)
b. c(1:5)
c. c(5-\>1)
d. c(1,2,3,4,5)
Answer: a. c(5:1)
OR
Q16. In R, which command
will read the file books-db.csv?
a. read.books-db.csv
b. read.csv (books-db.csv)
c. books-db.csv
d. return books-db.csv
Answer: b. read.csv
(books-db.csv)
Q17. In R, which command
removes a variable from memory?
a. detach
b. rm
c. drop
d. sd
Answer: b. rm
OR
Q18. n R, what is the
result of the function as.integer(3.3)?
a. 3
d. False
c. ‘3.3’
b. 3.3
Answer: a. 3
OR
Q19. Assume the array
books_array contains 6 elements. The array has three rows and two columns and
appears as follows:
[,1] [,2] [1,] “It” “Dr. Sleep” [2,] “Misery” “Carrie” [3,] “The Shining” “The
Mist”
If you input the books_array[,1] command, what will be the output?
a. “It”
b. “The Shining”
c. “It” “Dr. Sleep”
d. “It” “misery” “The Shining”
Answer: d. “It” “misery”
“The Shining”
Q20. One movie is 150
minutes long, and another is 90 minutes long. Using R, which of the following
commands would correctly calculate the difference in length, in seconds,
between the two films?
a. (150 – 90 \* 60)
b. (150 – 90) \* 60
c. 150 – 90 \* 60
d. 150 – (90 \* 60)
Answer: b. (150 – 90) \* 60
Q21. Assume the variable
books_vector is a vector that contains six elements. Which of the following
commands creates an array of this vector with three rows and two columns?
a. array(books_vector, dim = c(3, 2))
b. array(c(books_vector), dim = (2, 3))
c. array(books_vector, dim = c(2, 3))
d. array(books_vector, dim = (3,2))
Answer: a.
array(books_vector, dim = c(3, 2))
Q22. After installing and
calling the httr library in R, which command can you use to request information
about https://www.google.com?
a. BROWSE(“https://www.google.com/”)
b. GET(“https://www.google.com/”)
c. PATCH(“https://www.google.com/”)
d. PUT(“https://www.google.com/”)
Answer: b.
GET(“https://www.google.com/”)
OR
Q23. After installing and
calling the httr library in R, which method should you use to update a
resource?
a. BROWSE
b. GET
c. PUT
d. UPDATE
Answer: c. PUT
Q24. In R, what is the
result of the function as.numeric(TRUE)?
a. 1
b. 4
c. FALSE
d. NA
Answer: a. 1
OR
Q25. In R, assume you have
a vector named “age,” and each element in the vector is the age of one person
in a group. Which command must you use to map each person’s name to their
respective age?
a. call(age)
b. sink(age)
c. names(age)
d. print(age)
Answer: c. names(age)